
| Manned Flight No. | 132 |
| Manned flight of the USA No. | 65 |
| Manned flight Space Shuttle No. | 35 |
| Manned flight Discovery No. | 10 |
| Launch: | Apr 24, 1990 12:33:51 |
| Landing: | Apr 29, 1990 13:49:57 |
| Duration: | 5 d 1 h 16 m 6 s (121 h 16 m 6 s) |
| Orbits: | 80 |


| Manned Flight No. | 132 |
| Manned flight of the USA No. | 65 |
| Manned flight Space Shuttle No. | 35 |
| Manned flight Discovery No. | 10 |
| Launch: | Apr 24, 1990 12:33:51 |
| Landing: | Apr 29, 1990 13:49:57 |
| Duration: | 5 d 1 h 16 m 6 s (121 h 16 m 6 s) |
| Orbits: | 80 |

Loren Shriver (Commander)

Astronaut No. 156
Astronaut USA No. 85
Shriver: 2nd flight
Cumulative time: 8 d 2 h 49 m 29 s
(194 h 49 m 29 s)
Charles Bolden (Pilot)

Astronaut No. 196
Astronaut USA No. 117
Bolden: 2nd flight
Cumulative time: 11 d 3 h 19 m 57 s
(267 h 19 m 57 s)

Astronaut No. 146
Astronaut USA No. 76
Hawley: 3rd flight
Cumulative time: 17 d 4 h 16 m 1 s
(412 h 16 m 1 s)

Astronaut No. 133
Astronaut USA No. 67
McCandless: 2nd flight (last)
Cumulative time: 13 d 0 h 32 m 1 s
(312 h 32 m 1 s)

Astronaut No. 150
Astronaut USA No. 80
Woman-astronaut No. 5
Sullivan: 2-ый flight
Cumulative time: 13 d 6 h 39 m 44 s
(318 h 39 m 44 s)
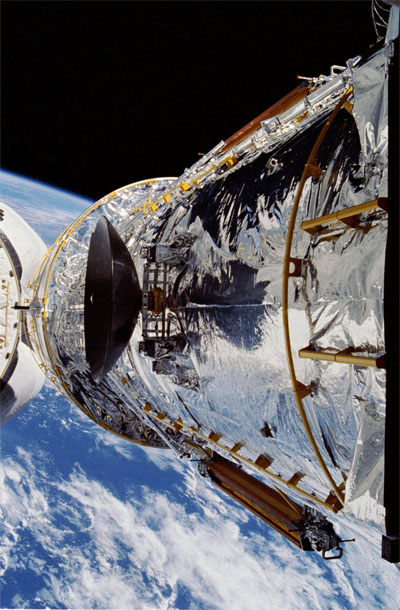

The Hubble telescope in the cargo bay of the shuttle Discovery.

Crew of the shuttle Discovery in orbit.
Thirty-fifth flight of the Space Shuttle. The tenth flight of the shuttle Discovery. Delivery of the Hubble Space Telescope into orbit.

US scientists and engineers are completing preparations for a space launch that will crown the hard work of nearly 20 years. From the launch site at Cape Canaveral aboard the Discovery reusable spacecraft to low-earth orbit the Hubble Astronomical Telescope will be launched.
Scientists compare their expectations in connection with the launch of the Hubble with the moment when Galileo first took a device invented by him for observing celestial bodies. As you know, he increased the severity of the human vision tenfold. "Hubble" will "see" objects 50 to 100 times smaller than those that are visible through the very a strong telescope located on the earth's surface. According to scientists, he will be able to distinguish from 5 to 10 trillion celestial objects (the human eye distinguishes only about 6 thousand).
Such broad capabilities of the new telescope are associated with the fact that it will be located outside the Earth's atmosphere and, of course, with its unique design, using all the latest technical achievements. The forty-three-foot telescope has reflector with a diameter of 94.5 inches and a secondary twelve-inch mirror, it is equipped with working chambers covering a wide of the light spectrum, a high-speed photometer and two spectrographs. The telescope is mounted on a satellite weighing 12 tons.
The design, development and practical creation of the "Hubble" was carried out by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) since 1972. The work was attended by 350 American and foreign scientific and industrial companies and firms. The total cost of the space telescope and its launch into space is $ 1.5 billion. Together with costs for ground structures and services, the project will cost $ 2.1 billion. Only a system of mathematical software the maintenance of the telescope cost $ 70 million. For the accuracy of its guidance, a program has been compiled containing a list out of 20 million "guiding stars". This work took 8 years.
The space telescope is named after the famous American astronomer Edwin Hubble, who substantiated the theory with his discoveries the expanding universe. The telescope will be launched into orbit 380 miles from the Earth's surface. As scientists expect, "Hubble" will serve science for about 15 years. Every five years, it will be serviced directly in orbit by specialists who will be delivered by the space shuttle. They will carry out preventive maintenance, install and change devices and equipment. According to the press, over 3,500 astronomers have expressed their readiness to submit their proposals for observations with the help of Hubble. So far, 162 proposals have been selected belonging to scientists from 21 countries.
A. BLINOV.

At Cape Canaveral (USA), a decision was announced to postpone the launch of the Discovery space shuttle with the unique Hubble telescope on board. Engineers at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) discovered a malfunction in one of the spacecraft's spare power supplies four minutes before launch. "We do not yet know what the consequences of the discovered defect will be," said prelaunch leader Robert Seek, "but the start will have to be postponed for at least a week or two." This is reported by news agencies.
The longest flight:
Dec 21, 1987 365 d 22 h 39 m 00 s (8782 h 39 m 0 s)
Vladimir Titov
and Musa Manarov
The largest number of flights: 6 Young
The most cumulative time in space (3 flightа):
430 d 18 h 15 m 30 s (10338 h 15 m 30 s)
Yuri Romanenko